Earthworks (archaeology) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In archaeology, earthworks are artificial changes in land level, typically made from piles of artificially placed or sculpted rocks and soil. Earthworks can themselves be archaeological features, or they can show features beneath the surface.
In archaeology, earthworks are artificial changes in land level, typically made from piles of artificially placed or sculpted rocks and soil. Earthworks can themselves be archaeological features, or they can show features beneath the surface.
 An accurate
An accurate
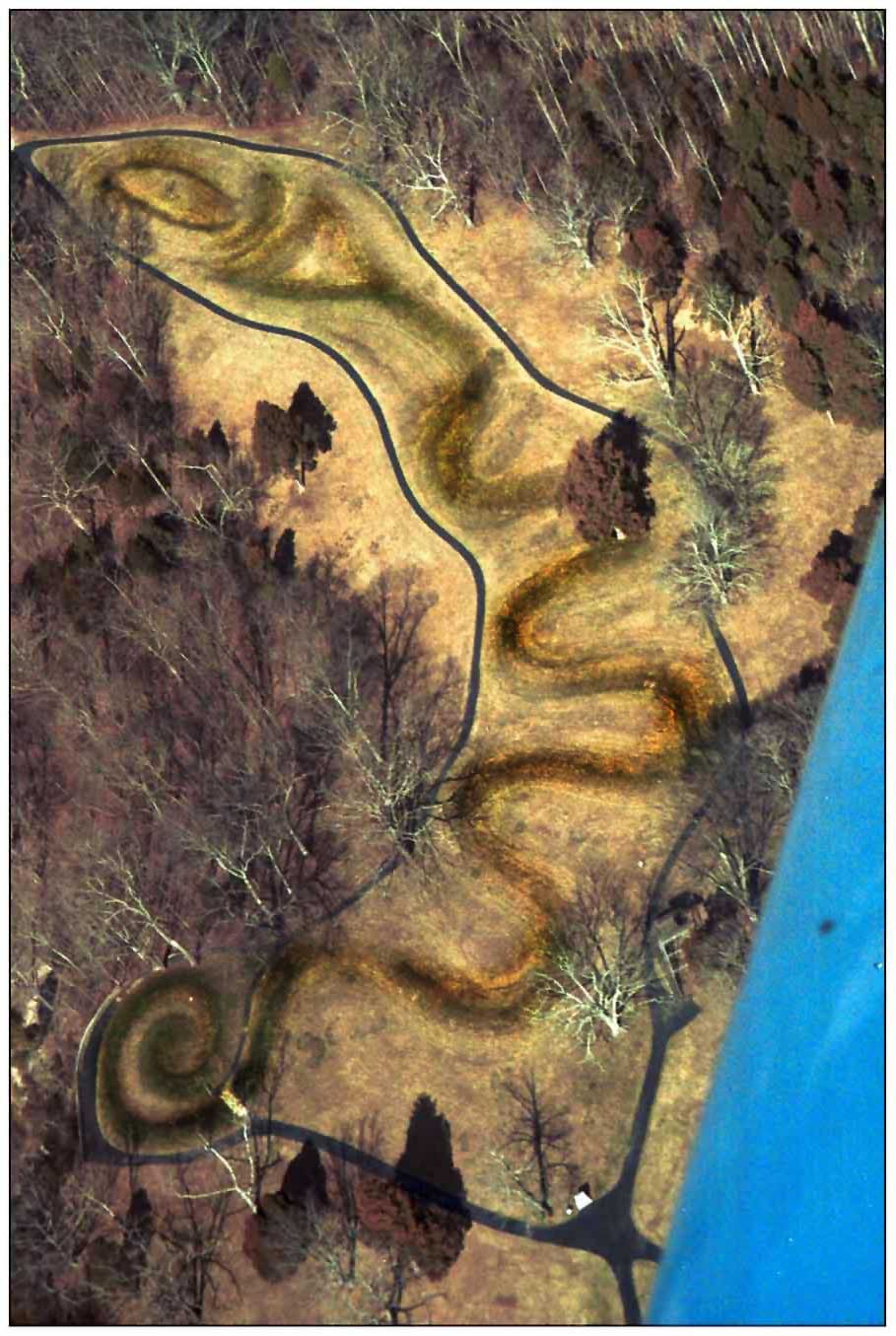 Earthworks in North America include
Earthworks in North America include
Image:Grodzisko w Bielsku-Białej.jpg, An 11th-century
Types
Earthworks of interest to archaeologists includehill fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
s, henge
There are three related types of Neolithic earthwork that are all sometimes loosely called henges. The essential characteristic of all three is that they feature a ring-shaped bank and ditch, with the ditch inside the bank. Because the internal ...
s, mound
A mound is a heaped pile of earth, gravel, sand, rocks, or debris. Most commonly, mounds are earthen formations such as hills and mountains, particularly if they appear artificial. A mound may be any rounded area of topographically higher ...
s, platform mound
Platform may refer to:
Technology
* Computing platform, a framework on which applications may be run
* Platform game, a genre of video games
* Car platform, a set of components shared by several vehicle models
* Weapons platform, a system or ...
s, effigy mound
An effigy mound is a raised pile of earth built in the shape of a stylized animal, symbol, religious figure, human, or other figure. The Effigy Moundbuilder culture is primarily associated with the years 550-1200 CE during the Late Woodland Peri ...
s, enclosures
Enclosure or Inclosure is a term, used in English landownership, that refers to the appropriation of "waste" or "common land" enclosing it and by doing so depriving commoners of their rights of access and privilege. Agreements to enclose land ...
, long barrow
Long barrows are a style of monument constructed across Western Europe in the fifth and fourth millennia BCE, during the Early Neolithic period. Typically constructed from earth and either timber or stone, those using the latter material repre ...
s, tumuli
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built ...
, ridge and furrow
Ridge and furrow is an archaeological pattern of ridges (Medieval Latin: ''sliones'') and troughs created by a system of ploughing used in Europe during the Middle Ages, typical of the open-field system. It is also known as rig (or rigg) and f ...
, mottes, round barrows, and other tomb
A tomb ( grc-gre, τύμβος ''tumbos'') is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called ''immureme ...
s.
* Hill fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
s, a type of fort made out of mostly earth and other natural materials including sand, straw, and water, were built as early as the late Stone Age and were built more frequently during the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
and Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
as a means of protection. See also Oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (plural ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretchi ...
.
* Henge
There are three related types of Neolithic earthwork that are all sometimes loosely called henges. The essential characteristic of all three is that they feature a ring-shaped bank and ditch, with the ditch inside the bank. Because the internal ...
earthworks are those that consist of a flat area of earth in a circular shape that are encircled by a ditch, or several circular ditches, with a bank on the outside of the ditch built with the earth from inside the ditch. They are believed to have been used as monuments for spiritual ritual ceremonies.
* A mound
A mound is a heaped pile of earth, gravel, sand, rocks, or debris. Most commonly, mounds are earthen formations such as hills and mountains, particularly if they appear artificial. A mound may be any rounded area of topographically higher ...
is a substantial manmade pile of earth or rocks that was frequently created to mark burial sites
* Platform mound
Platform may refer to:
Technology
* Computing platform, a framework on which applications may be run
* Platform game, a genre of video games
* Car platform, a set of components shared by several vehicle models
* Weapons platform, a system or ...
s are pyramid or rectangular-shaped mounds that are used to hold a building or temple on top.
* An effigy mound
An effigy mound is a raised pile of earth built in the shape of a stylized animal, symbol, religious figure, human, or other figure. The Effigy Moundbuilder culture is primarily associated with the years 550-1200 CE during the Late Woodland Peri ...
is a pile of earth, often very large in scale, that is shaped into the image of a person or animal, often for symbolic or spiritual reasons
* An enclosure is a space that is surrounded by an earthwork.
* Long barrows are oblong-shaped mounds that are used for burials.
* A tumulus
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones bu ...
or barrow is a mound of earth created over a tomb.
* A cross dyke
A cross dyke or cross-dyke (also referred to as a cross-ridge dyke, covered way, linear ditch, linear earthwork or spur dyke) is a linear earthwork believed to be a prehistoric land boundary that usually measures between in length. A typical cr ...
or cross-ridge dyke is a bank and ditch, or sometimes a ditch between two banks, that crosses a ridge or spur of high ground. Found in Europe and often belonging to the later Bronze Age or Iron Age. Often marked on Ordnance Survey
Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (see ordnance and surveying), which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of 1745. There was a ...
maps in the UK.
* Ridge and furrow
Ridge and furrow is an archaeological pattern of ridges (Medieval Latin: ''sliones'') and troughs created by a system of ploughing used in Europe during the Middle Ages, typical of the open-field system. It is also known as rig (or rigg) and f ...
s are sets of parallel depressions and ridges in the ground formed primarily through historic farming techniques.
* Mottes are mound
A mound is a heaped pile of earth, gravel, sand, rocks, or debris. Most commonly, mounds are earthen formations such as hills and mountains, particularly if they appear artificial. A mound may be any rounded area of topographically higher ...
structures made of earth and stone that once held castles. They are an important part of the motte-and-bailey castle
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy t ...
, a castle design during early Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
times in which the castle is built on the motte, and surrounded by a ditch and a bailey, which is an enclosure with a stone wall.
* A round barrow is a mound that is in a rounded shape that was used during Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
times as a burial mound.
* Geoglyph
A geoglyph is a large design or motif (generally longer than 4 metres) produced on the ground by durable elements of the landscape, such as stones, stone fragments, gravel, or earth. A positive geoglyph is formed by the arrangement and alignmen ...
, a large design or motif
Size
Earthworks can vary in height from a few centimetres to the size ofSilbury Hill
Silbury Hill is a prehistoric artificial chalk mound near Avebury in the English county of Wiltshire. It is part of the Stonehenge, Avebury and Associated Sites UNESCO World Heritage Site. At high, it is the tallest prehistoric man-made mound ...
at . They can date from the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
to the present. The structures can also stretch for many tens of miles (e.g. Offa's Dyke
Offa's Dyke ( cy, Clawdd Offa) is a large linear earthwork that roughly follows the border between England and Wales. The structure is named after Offa, the Anglo-Saxon king of Mercia from AD 757 until 796, who is traditionally believed to ha ...
and Antonine Wall). In area, they can cover many hectares; for example, Maiden Castle, which is .
Detection
Shallow earthworks are often more visible ascropmarks
Cropmarks or crop marks are a means through which sub-surface archaeological, natural and recent features may be visible from the air or a vantage point on higher ground or a temporary platform. Such marks, along with parch marks, soil marks a ...
or in aerial photographs
Aerial photography (or airborne imagery) is the taking of photographs from an aircraft or other airborne platforms. When taking motion pictures, it is also known as aerial videography.
Platforms for aerial photography include fixed-wing aircra ...
if taken when the sun is low in the sky and shadows are more pronounced. Similarly, earthworks may be more visible after a frost or a light dusting of snow.
Earthworks can be detected and plotted using Light Detection and Ranging ( LIDAR). This technique is particularly useful for mapping small variations in land height that would be difficult to detect by eye. It can be used to map features beneath forest canopy and for features hidden by other vegetation. LIDAR results can be input into a geographic information system ( GIS) to produce three-dimensional representations of the earthworks.
Interpretation
 An accurate
An accurate survey
Survey may refer to:
Statistics and human research
* Statistical survey, a method for collecting quantitative information about items in a population
* Survey (human research), including opinion polls
Spatial measurement
* Surveying, the techniq ...
of the earthworks can enable them to be interpreted without the need for excavation. For example, earthworks from deserted medieval villages can be used to determine the location, size, and layout of lost settlements. Often these earthworks can point to the purpose of such a settlement, as well the context in which it existed.
Examples
 Earthworks in North America include
Earthworks in North America include mound
A mound is a heaped pile of earth, gravel, sand, rocks, or debris. Most commonly, mounds are earthen formations such as hills and mountains, particularly if they appear artificial. A mound may be any rounded area of topographically higher ...
s built by Native Americans known as the Mound Builders
A number of pre-Columbian cultures are collectively termed "Mound Builders". The term does not refer to a specific people or archaeological culture, but refers to the characteristic mound earthworks erected for an extended period of more than 5 ...
. Ancient people who lived in the American Midwest commonly built effigy mound
An effigy mound is a raised pile of earth built in the shape of a stylized animal, symbol, religious figure, human, or other figure. The Effigy Moundbuilder culture is primarily associated with the years 550-1200 CE during the Late Woodland Peri ...
s, which are mounds shaped like animals (real or imaginary) or people. Possibly the most famous of these effigy mounds is Serpent Mound
The Great Serpent Mound is a 1,348-foot-long (411 m), three-foot-high prehistoric effigy mound located in Peebles, Ohio. The mound itself resides on the Serpent Mound crater plateau, running along the Ohio Brush Creek in Adams County, Ohio. ...
. Located in Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, this earthen work is thought to memorialize alignments of the planets and stars that were of special significance to the Native Americans that constructed it. Cone-shaped or conical mound
A cone is a three-dimensional geometric shape that tapers smoothly from a flat base (frequently, though not necessarily, circular) to a point called the apex or vertex.
A cone is formed by a set of line segments, half-lines, or lines co ...
s are also numerous, with thousands of them scattered across the American Midwest, some over tall. These conical mounds appear to be marking the graves of one person or even dozens of people. An example of a conical mound is the Miamisburg Mound in central Ohio, which has been estimated to have been built by people of the Adena culture
The Adena culture was a Pre-Columbian Native American culture that existed from 500 BCE to 100 CE, in a time known as the Early Woodland period. The Adena culture refers to what were probably a number of related Native American societies sharing ...
in the time range of 800 B.C. to 100 AD. The American Plains also hold temple mounds, or platform mound
Platform may refer to:
Technology
* Computing platform, a framework on which applications may be run
* Platform game, a genre of video games
* Car platform, a set of components shared by several vehicle models
* Weapons platform, a system or ...
s, which are giant pyramid-shaped mounds with flat tops that once held temples made of wood. Examples of temple mounds include Monks Mound
Monks Mound is the largest Pre-Columbian earthwork in the Americas and the largest pyramid north of Mesoamerica. The beginning of its construction dates from 900–955 CE. Located at the Cahokia Mounds UNESCO World Heritage Site near Collinsvil ...
located at the Cahokia
The Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site ( 11 MS 2) is the site of a pre-Columbian Native American city (which existed 1050–1350 CE) directly across the Mississippi River from modern St. Louis, Missouri. This historic park lies in south- ...
site in Collinsville, Illinois,Feder, 54 and Mound H at the Crystal River site in Citrus County
Citrus County is a county located on the west central coast of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 153,843. Its county seat is Inverness, and its largest community is Homosassa Springs.
Citrus County compris ...
, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
. The earthworks at Poverty Point
Poverty Point State Historic Site/Poverty Point National Monument (french: Pointe de Pauvreté; 16 WC 5) is a prehistoric earthwork constructed by the Poverty Point culture, located in present-day northeastern Louisiana, though evidence of t ...
occupy one of the largest-area sites in North America, as they cover some 920 acres (320 ha) of land in Louisiana.
Military earthworks can result in subsequent archaeological earthworks. Examples include Roman marching forts which can leave small earthworks. During the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states ...
, earthwork fortifications were built throughout the country, by both Confederate
Confederacy or confederate may refer to:
States or communities
* Confederate state or confederation, a union of sovereign groups or communities
* Confederate States of America, a confederation of secessionist American states that existed between 1 ...
and Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
sides. The largest earthwork fort built during the war was Fortress Rosecrans, which originally encompassed .
In northeastern Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
, near the city of Bosaso
Bosaso ( so, Boosaaso, ar, بوصاصو), historically known as Bender Cassim is a city in the northeastern Bari province ('' gobol'') of Somalia. It is the seat of the Bosaso District. Located on the southern coast of the Gulf of Aden, the mu ...
at the end of the Baladi valley, lies an earthwork long. Local tradition recounts that the massive embankment marks the grave of a community matriarch. It is the largest such structure in the wider Horn
Horn most often refers to:
*Horn (acoustic), a conical or bell shaped aperture used to guide sound
** Horn (instrument), collective name for tube-shaped wind musical instruments
*Horn (anatomy), a pointed, bony projection on the head of various ...
region.
Bigo bya Mugenyi is an extensive earthworks site in the interlacustrine region of southwestern Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa. The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The sou ...
. On the south shore of the Katonga river, the Bigo earthworks consist of a series of ditches and berms comprising an outer arch that encompasses four interconnected enclosures. When combined, the Bigo earthworks measure more than long. Radiometric
Radiometry is a set of techniques for measuring electromagnetic radiation, including visible light. Radiometric techniques in optics characterize the distribution of the radiation's power in space, as opposed to photometric techniques, which ch ...
dates from archaeological investigations at Bigo date the earthworks to roughly AD 1300 - 1500, and they have been called Uganda's "largest and most important ancient monument".
The Steppe Geoglyphs, discovered in 2007 using Google Earth, are an example of earthworks in Central Asia.
Gallery
hill fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
: Bielsko-Biała
Bielsko-Biała (; cs, Bílsko-Bělá, german: Bielitz-Biala, szl, Bjylsko-Bjoło) is a city in southern Poland, with a population of approximately 168,319 as of December 2021, making it the 22nd largest city in Poland, and an area of . It is a ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
Image:Chateau-de-Gisors.jpg, A 12th-century motte-and-bailey castle
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively easy t ...
: Château de Gisors in Eure, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
Image:Grave Creek Mound.jpg, An Adena Adena may refer to:
Artists
* ADENA, Romanian singer-songwriter
*Adeena Karasick (born 1965), Canadian poet, performance artist, and essayist
* Adena Halpern (born 1968), American author
*Adena Jacobs (born 1982), Australian theatre director
Place ...
tumulus
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones bu ...
(burial mound): Grave Creek Mound
The Grave Creek Mound in the Ohio River Valley in West Virginia is one of the largest conical-type burial mounds in the United States, now standing high and in diameter. The builders of the site, members of the Adena culture, moved more than 60,0 ...
in West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
, U.S.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
Image:Monks Mound in July.JPG, A Mississippian platform mound
Platform may refer to:
Technology
* Computing platform, a framework on which applications may be run
* Platform game, a genre of video games
* Car platform, a set of components shared by several vehicle models
* Weapons platform, a system or ...
: Cahokia
The Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site ( 11 MS 2) is the site of a pre-Columbian Native American city (which existed 1050–1350 CE) directly across the Mississippi River from modern St. Louis, Missouri. This historic park lies in south- ...
in Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
, U.S.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
Image:17 08 192 ocmulgee.jpg, Temple Mound at Ocmulgee National Monument
Ocmulgee Mounds National Historical Park (formerly Ocmulgee National Monument) in Macon, Georgia, United States preserves traces of over ten millennia of culture from the Native Americans in the Southeastern Woodlands. Its chief remains are majo ...
Image:Serpent Mound1 HRoe 2005.jpg, A Fort Ancient
Fort Ancient is a name for a Native American culture that flourished from Ca. 1000-1750 CE and predominantly inhabited land near the Ohio River valley in the areas of modern-day southern Ohio, northern Kentucky, southeastern Indiana and western ...
effigy mound
An effigy mound is a raised pile of earth built in the shape of a stylized animal, symbol, religious figure, human, or other figure. The Effigy Moundbuilder culture is primarily associated with the years 550-1200 CE during the Late Woodland Peri ...
: Serpent Mound
The Great Serpent Mound is a 1,348-foot-long (411 m), three-foot-high prehistoric effigy mound located in Peebles, Ohio. The mound itself resides on the Serpent Mound crater plateau, running along the Ohio Brush Creek in Adams County, Ohio. ...
in Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
, U.S.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
Image:Stoney Littleton.jpg, A Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
long barrow
Long barrows are a style of monument constructed across Western Europe in the fifth and fourth millennia BCE, during the Early Neolithic period. Typically constructed from earth and either timber or stone, those using the latter material repre ...
: Stoney Littleton Long Barrow in Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
, U.K.
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
Image:Thornborough Henge.jpg, A Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
henge
There are three related types of Neolithic earthwork that are all sometimes loosely called henges. The essential characteristic of all three is that they feature a ring-shaped bank and ditch, with the ditch inside the bank. Because the internal ...
: Thornborough Henges
The Thornborough Henges are an unusual ancient monument complex that includes the three aligned henges that give the site its name. The complex is located near the village of Thornborough, close to the town of Masham in North Yorkshire, Engla ...
in North Yorkshire
North Yorkshire is the largest ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county (lieutenancy area) in England, covering an area of . Around 40% of the county is covered by National parks of the United Kingdom, national parks, including most of ...
, U.K.
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
Citations
General and cited references
* Aston, Mick (2002). ''Interpreting the Landscape'', Tempus, * Feder, Kenneth (2008). ''Linking to the Past'', 2nd ed., New York: Oxford, * Muir, Richard (2004). ''Landscape Encyclopedia'', Bollington, Cheshire: Windgather, * Taylor, Christopher (1974). ''Fieldwork in Medieval Archaeology'', London: Batsford, * Wilson, D. R. (2000). ''Air Photo Interpretation for Archaeologists'', 2nd ed., Stroud: Tempus, * Wood, Eric (1975). ''Collins Field Guide to Archaeology'', 4th ed., London: Collins,External links
* {{Authority control Archaeological features